Lifecycle hooks
Hooks let you “hook into” Prisma-AppSync lifecycle to either trigger custom business logic or manipulate data at runtime.
👉 Example code
Basic example:
ts
return await prismaAppSync.resolve({
event,
hooks: {
// Mutate Post title before creation on database
'before:createPost': async (params: BeforeHookParams) => {
params.prismaArgs.data.title = 'New post title'
return params
},
// Override query result using always the same Post title
'after:listPosts': async (params: AfterHookParams) => {
params.result = params.result.map(r => r.title = 'Always the same title')
return params
},
},
})Advanced example:
ts
return await prismaAppSync.resolve<'likePost'>({
event,
hooks: {
// execute before any query
'before:**': async (params: BeforeHookParams) => params,
// execute after any query
'after:**': async (params: AfterHookParams) => params,
// execute after custom resolver query `likePost`
// (e.g. `query { likePost(postId: 3) }`)
'after:likePost': async (params: AfterHookParams) => {
await params.prismaClient.notification.create({
data: {
event: 'POST_LIKED',
targetId: params.args.postId,
userId: params.authIdentity.sub,
},
})
return params
},
},
})👉 Types
ts
export interface QueryParams {
type: GraphQLType
operation: string
context: Context
fields: string[]
paths: string[]
args: any
prismaArgs: PrismaArgs
authorization: Authorization
identity: Identity
headers: any
prismaClient: PrismaClient
}
type BeforeHookParams = QueryParams
type AfterHookParams = QueryParams & {
result: any | any[]
}👉 Usage rules
Hooks are made of a Path (e.g.
after:updatePost) and an async function.Path syntax always starts with
before:orafter:.beforeorafterquerying data from the database.Path syntax after
:uses Micromatch syntax.Hooks are fully typed, so VSCode IntelliSense will give you the full list of Hooks Paths you can use while typing. Example:
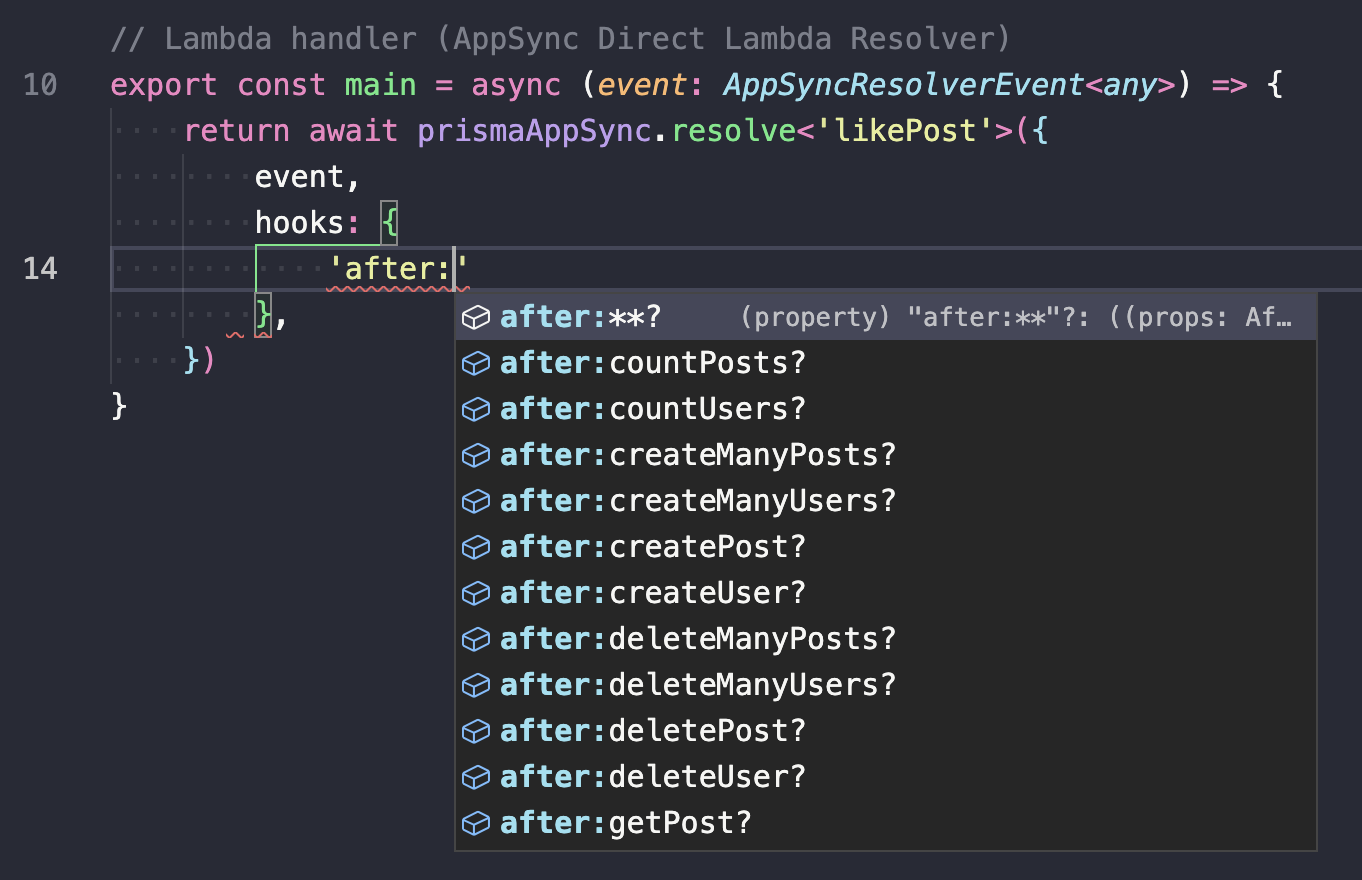
- Hooks functions all receive a single object as a parameter. Here is an example object received inside
after:getPost:
json
{
"type": "Query",
"operation": "getPost",
"context": { "action": "get", "alias": "access", "model": "Post" },
"fields": ["title", "status"],
"paths": ["get/post/title", "get/post/status"],
"args": { "where": { "id": 5 } },
"prismaArgs": {
"where": { "id": 5 },
"select": { "title": true, "status": true }
},
"authorization": "API_KEY",
"identity": {},
"result": { "title": "My first post", "status": "PUBLISHED" }
}- Key
resultis only available insideafterhooks. - Hooks async functions MUST return the object received as a parameter (either mutated or untouched).
- Using hooks on custom resolvers requires explicitly listing resolvers using a TypeScript Generic
prismaAppSync.resolve<T>:
ts
// Using custom resolver `likePost`
return await prismaAppSync.resolve<'likePost'>({ event, hooks })
// Using multiple custom resolvers
return await prismaAppSync.resolve<'likePost' | 'unlikePost'>({ event, hooks })